Lecture
L1
All teams followed the same process: (academic) XP (Extreme Programming)
Default process: XP
- pigs即为项目组的实际参与人员,chickens 为项目组的外部人员,包括经理、最终用户等等。
- Story, Planning, Test-first, pair-prog, continuous integration, refactoring
- Work product: User stories, tests, code
Responsibility
产品经理:项目初始化,项目监督与控制,软件质量管理
开发部门:需求,设计,实现
后开发:安装,操作与 support,维护,retirement
整体进度:验证与确认,软件配置,文档
IEEE 610: “The application of a systematic 系统的, disciplined 有纪律的, quantifiable可量化的 approach to the development 开发, operation 操作, and maintenance 维护 of software.”
L2
Software configuration management (SCM)
- Change control
- Version control
- Building
- Releasing
Version Control System
- SVN:Apache Subversion
| 命令 |
|---|
| svn checkout <address_to_remote> <name_of_local_dir> |
| git checkout <branch_name> |
| svn commit –m “msg” |
| git commit –m “msg” (git commit 召唤出 vim 编辑器可以更有条理的写 commit) |
| svn up |
| git pull upstream master |
| svn add <file_name> |
| git add <file_name> |
| Other command |
| svn st: shows the status of files in the current svn directory |
| svn rm: removes a file from the set of tracked files (will be removed on the remote server as well) |
| svn mv: moves a file from one directory to another (or renames if in same directory) |
| svn diff: diff between two revisions, or diff a file to see uncommitted local changes. (git diff) |
| svn status: shows you the status of the files in the directory subtree you are in (and not the entire repo). (git status) |
-
Git uses a distributed model
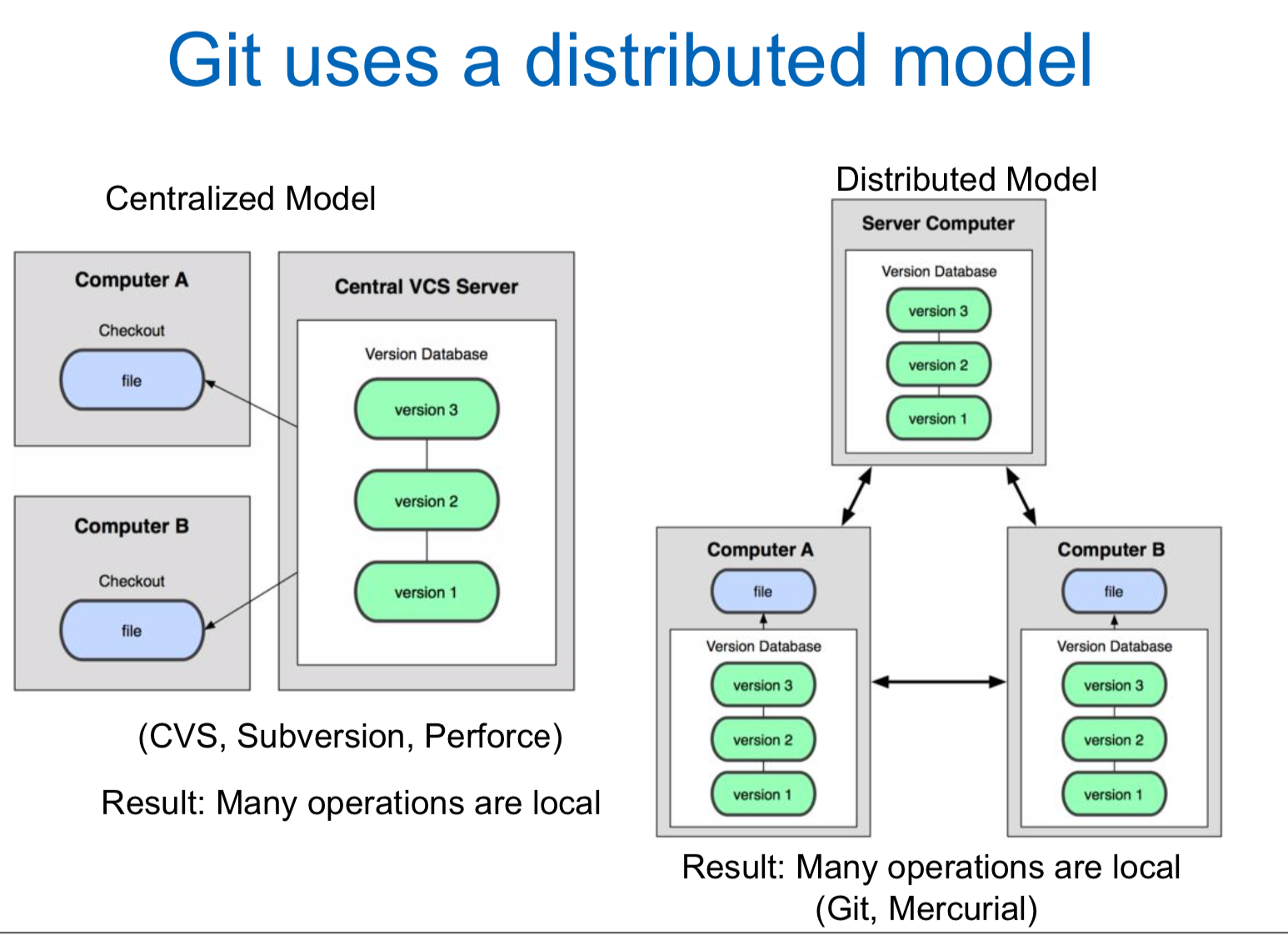
-
Git uses checksums
1677b2d: blahblahblah
-
git lifecycle
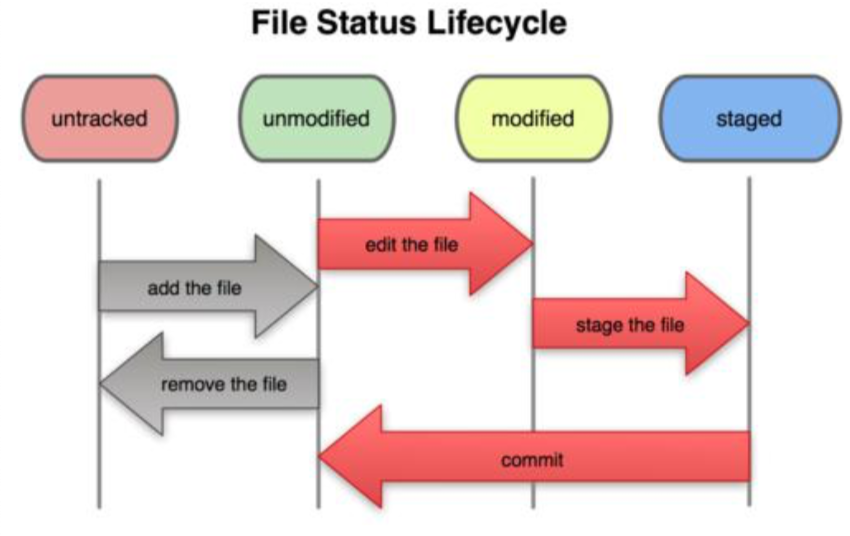
-
Git takes snapshot of every version of every files, but svn does not.
-
A Local Git project has three areas
Working directory——stagefile——>staging area
staging area——commit——>git dir(repo)
git dir(repo)——checkout proj——>Working directory
Pull Request
- tell others about changes you’ve pushed
- parties can review the set of changes 代码审查
- discuss potential modifications, and even push follow-up commits
git basic workflow
- Modify files in your working directory.
- Stage files, adding snapshots of them to your staging area.
- Do a commit, which takes the files as they are in the staging area and stores that snapshot permanently to your Git directory.
SVN vs. Git
| central repository approach | Distributed repository approach |
|---|---|
| check out local copies of the current version | checkout full fledged repository, complete with history |
| Greater redundancy and speed | |
| Branching and merging |
Parallel work
- One solution (locking): Impossible!
- Another solution (merging)
- Merging can be bad because sometimes it produces errors
-
- Two people change same line. System will force the one merging the changes to perform the merge manually.
-
- Changes don’t seem to conflict, but merging causes a bug.
-
Building
Building should be automatic
Gradle, ant, mvn
Daily build and smoke test
Software product 有什么产出
- Code
- Test suites
- Operation manuals (admins, end-users)
- Requirements
- Specifications
- Design documentation
- Plans/schedules
SCM
- Keep track of how software changes
- able to reproduce any version of the software
Branches
- Traditional advice for old version control
- Avoid (long-lived) branches if possible
- Modern version control (Git, HG…)
- Encourage use of (short-lived) branches
- Good reasons to branch
- Fixing bugs in customer version
- Experimental version
- Political fights
Identification
What is the relationship between items?
- Versions: tiny changes or function/feature completion
- Baseline: is a software configuration item that has been reviewed
and agreed upon, and that can be changed only through formal
change control procedures - Release: a software configuration item that the developers give to
other people (and also it should be a baseline)
Change Control
- Change request/engineering change order
- New feature
- Bug report
- Change control authority - decides which changes should be carried out
- Should link code changes to change requests
SCM Requirement
- Bureaucracy
- Discipline/training
- Tools
- Version control – cvs, subversion, git…
- Change control – bugzilla, mantis, jira…
- Building – make, ant, mvn…
- Releasing – Maven Central and Nexus…
Various Test
- Smoke Test: 确保整个系统在更改过后能运行(表面上来说没 bug)减少后期测试压力
- Unit test: 确保更改后模块仍能运行,没有错误
- Regression test: Ensure that existing code doesn’t get worse as you make other improvements 重新按照前一轮的测试用例再测试一遍
Codeline Policy
- Active Development Line
- Release Line
- Holds bug fixes for a release
- Private Versions
- Task Branch
- Hide a disruptive task from the rest of the team
- Release Prep Codeline
L3
Waterfall Process Activity
- Requirements – what software should do
- Design – structure code into modules; architecture
- Implementation – hack code
- Integration – put modules together
- Testing – check if code works
- Maintenance – keep making changes
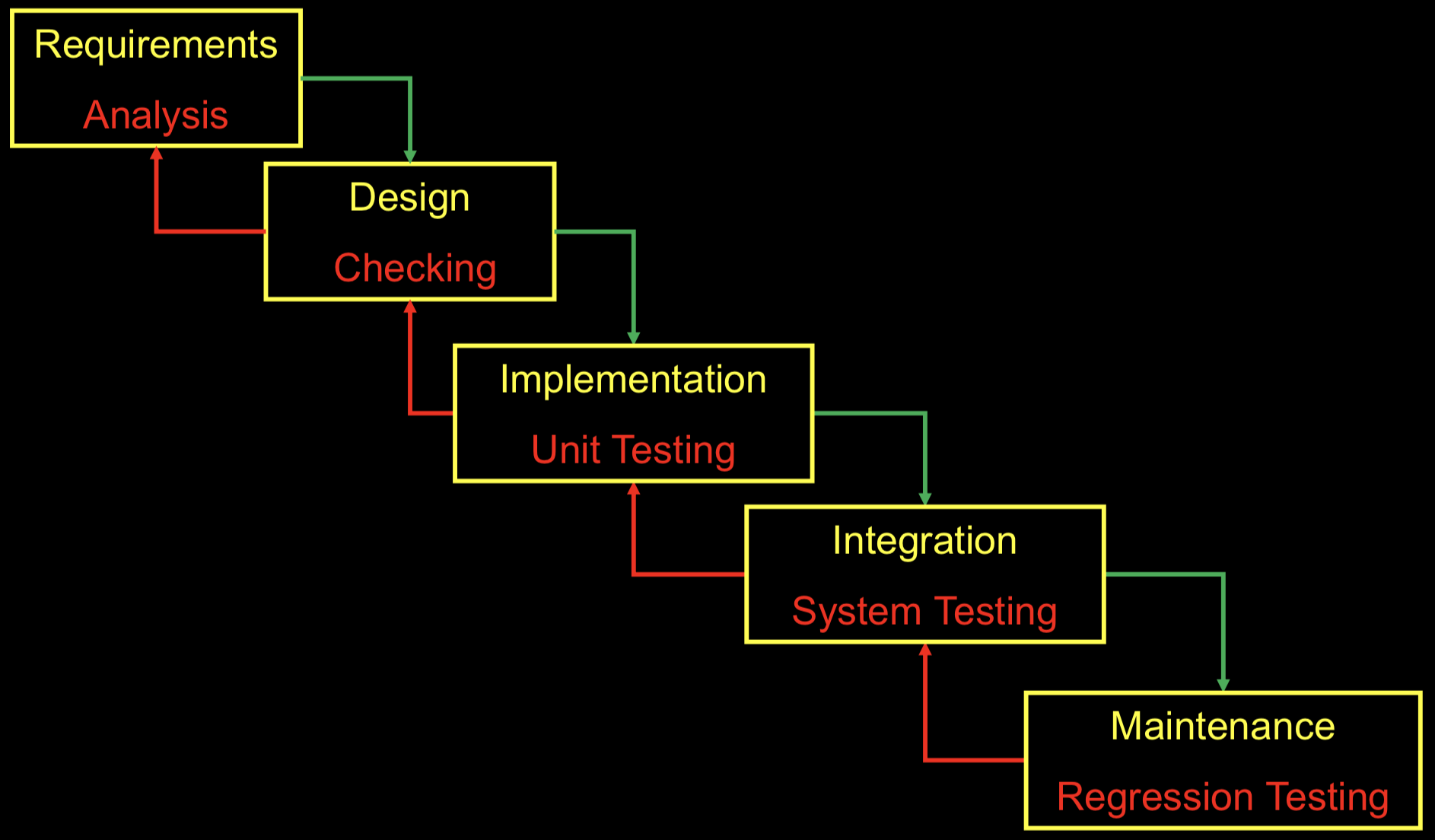
Extreme Programming (XP)
- Radically different from the rigid waterfall process
- Replace it with a collaborative and iterative design process
- Main ideas
- Don’t write much documentation
- Working code and tests are the main written product
- Implement features one by one
- Release code frequently
- Work closely with the customer
- Communicate a lot with team members
- Don’t write much documentation
Iterative Process
- Iteration = two week cycle (1-3 weeks)
- Plan each iteration in an iteration meeting that is held at the start of the iteration
- Iteration is going to implement set of user stories
- Divide work into tasks small enough to finish in a day
- Each day, programmers work in pairs to finish tasks
Pair Programming
Pair programming is a simple, straightforward concept. Two programmers work side-by-side at one computer, continuously collaborating on the same design, algorithm, code, and test. It allows two people to produce a higher quality of code than that produced by the summation of their solitary efforts.
| Driver | Navigator |
|---|---|
| types or writes | observer (looking for tactical & strategic defects) |
- 周期性角色转换
- 30分钟左右
- 一起写代码,设计,debug,测试
BENEFITS
- Higher product quality
- Improved cycle time
- Increased programmer satisfaction
- Enhanced learning
- Pair rotation
- Ease staff training and transition
- Knowledge management/Reduced product risk
- Enhanced team building
Why Pair works?
- Pair pressure
- Pair negotiation
- Pair Courage
- Pair Reviews
- Pair Debugging
- Pair-Learning
User Story
A user story represents: A feature customers want in the software
the smallest amount of information (a step) necessary to allow the customer to define (and steer) a path through the system
Written by customers (on index cards)

Concept
- Story point: unit of measure for expressing the overall size of a user story, feature, or other piece of work. The raw value of a story point is unimportant. What matters are the relative values.
- Related to how hard it is and how much of it there is
- Not related to amount of time or the number of people
- Unitless, but numerically-meaningful
- Ideal time: the amount of time “something” takes when stripped of all peripheral activities 排除所有外部干扰
- Elapsed time: the amount of time that passes on the clock to do “something” 实际时间 wall clock
- Velocity: measure of a team’s rate of progress, calculated by summing the number of story points assigned to each user story that the team completed during the operation. (5 story point / two-week iteration)
Estimating story point
Estimating ideal date
Deriving an estimate for a user story
- Expert opinion
- Analogy
- Disaggregation
- Planning poker 1,2,3,5,8,13,20,40,100
PLANNING GAME
- Customer writes user stories 用户来写
- Programmers estimate time to do each story 程序员来预估
- If story is too big, customer splits it 用户分割 story
- Customer chooses stories to match project velocity 用户选择 story
- Project velocity is amount of work done in the previous iteration(s)
- 程序员一个时刻只需要关心一个 iteration
- Customer can plan as many iterations as desired, but can change future
iterations
Unit Test and Refactoring
- To recover simplicity, you must refactor the code
- To refactor safely, you should have a rigorous set of unit tests
All software has automated (unit) tests
All tests pass, all the time, and Never check in broken code
How to work on a task
- Get latest version of the code. All tests pass.
- Write test first. It fails.
- Write code to make test pass. Now all tests pass.
- Refactor (clean up)
- Check in your code
先写测试,再写代码
L4 Test
Why Test?
- Improve quality
- Measure quality
- Learn the software
What is a test?
DEF: Run program with known inputs (test inputs/data), check results (with test oracles)
Tests pass (green) or fail (red)
Tests can document faults and code
Terms
MISTAKE 被程序员制造
FAULT/BUG 在程序代码中出现
FAILURE 在程序运行时发生
ERROR 就是与预期结果不符的差异
使用 JUnitTest
可重复的自动化测试
用来写 test driver 的一个结构
特性:
- Assertions for testing expected results
- Sharing common test data among tests
- Test suites for easily organizing and running tests
- Test runners, both graphical and textual
JUnit 可以用来测试整个对象,对象的一部分,不同对象之间的交互
每个 test 被嵌入一个 test method
一个 test class 有很多 test methods
test class 包括
- main() test runner
- 一堆 test methods
- Methods to set up the state before and update the state after each test and before and after all tests
JUNIT TEST FIXTURES
test fixture 是 test 的一个 state
- 有可能测试类中的 objects 和 variables 会被很多 test method 使用
- 初始化 (prefix values)
- 重置 (postfix values)
这样使得不同的 test method 不会共享 object 的 state
Objects in fixtures declared as instance variables
- They should be initialized in a @Before method
- JUnit runs them before every @Test method
- Can be deallocated or reset in an @After method
- JUnit runs them after every @Test method
所以说,不要把所有独立测试放到一个 method 中。在没有 automation 的情况下,放进一个 method 会有助于减少时空复杂度。但在有 automation 的情况下,small test 有利于我们更容易的辨别不同种类的 failures
使用 test runner
1 | // This section declares all of the test classes in the program. |
JUnite Assertion patterns
State Testing Patterns
- Final State Assertion: 最终结果断言
- Guard Assertion: 同时
@Before和@After断言 - Delta Assertion: 验证一个与 State 相关的变化
- Custom Assertion: 自定义
Interaction Assertions: 验证预期的反应
JUnit PARAMETERIZED TESTS 参数化测试
1 |
|
对于测试相似的变量的时候,避免代码臃肿
对于上面代码块所示,不用写若干个独立测试,而使用 @Parameters 声明一个测试集
JUNIT THEORIES
1 | public void removeThenAddDoesNotChangeSet( |
1 |
|
1 |
|
之前的 test 都是在 method 中硬编码测试数据,PARAMETERIZED 是实例化测试类本身
这里介绍 Contract Model: Assume, Act, Assert
- Assumptions (Preconditions) Limit Values Appropriately
- Action Performs Activity Under Scrutiny
- Assertions (Postconditions) Check Result
@Theory 绑定 @DataPoint 以达到从外部传参的目的
Test Driven Development (TDD)
Kent Beck’s rules
Never write a single line of code unless you have a failing automated test.
Eliminate duplication.
Steps in TDD
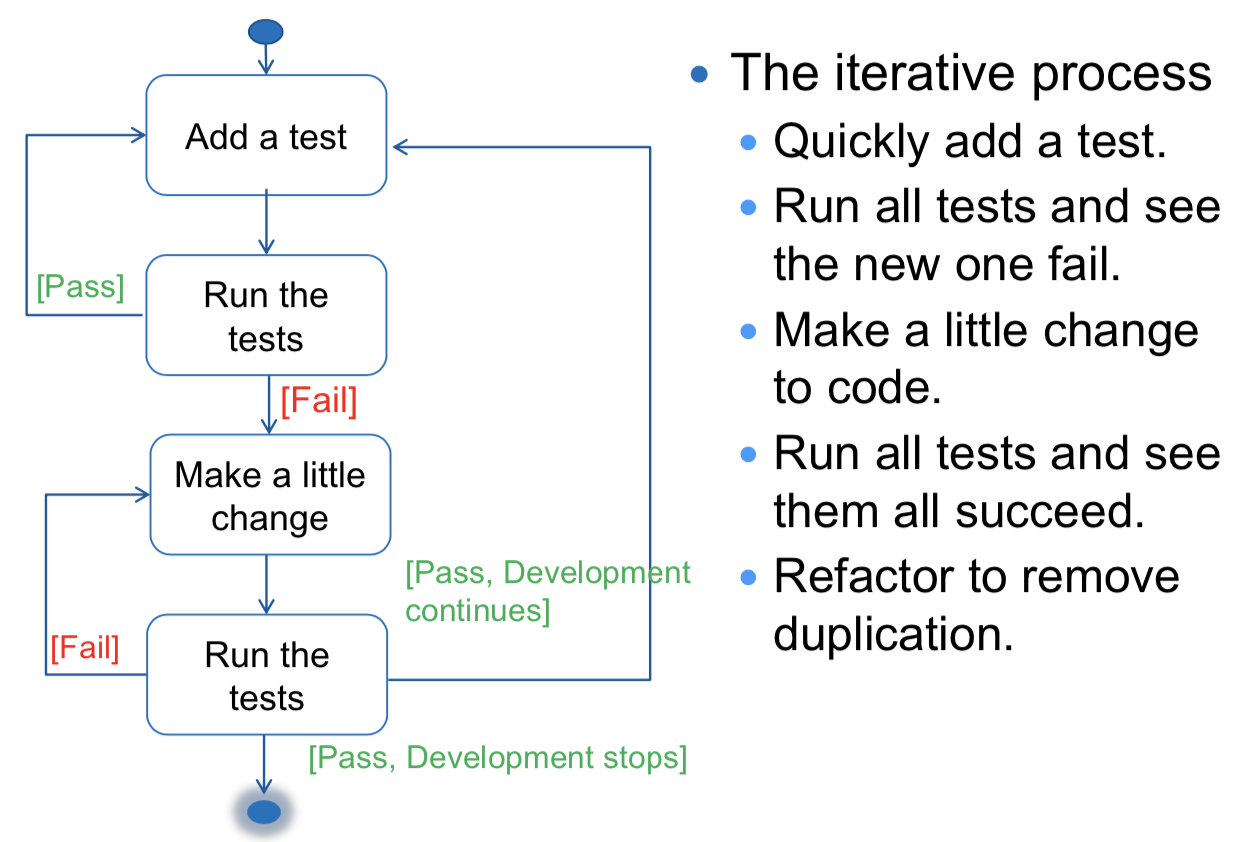
L5
Each test should be independent of each other. (Independent instance)
Any given behaviour should be specified in one and only one test.
Correct method signature should be assertEquals(expected,actual)
Use assertEquals(A, B) to compare strings, but not assertTrue(boolean expression)
Code Coverage
DEF: Code Coverage 是一种衡量方法来描述当运行一个特别的 test suite (一种动态分析)的时候,有多少(哪些)代码被运行了。这是一种 white box test,Testing where internal structure/ design/ implementation of the item being tested is known
Coverage = Reachability (可达性)
- 可以知道哪些代码没被测试到
- improve coverage 以达到提高代码质量的目的
- 辨别 testing gap 和 missing test
- 辨别冗长的、冗余的(dead)代码
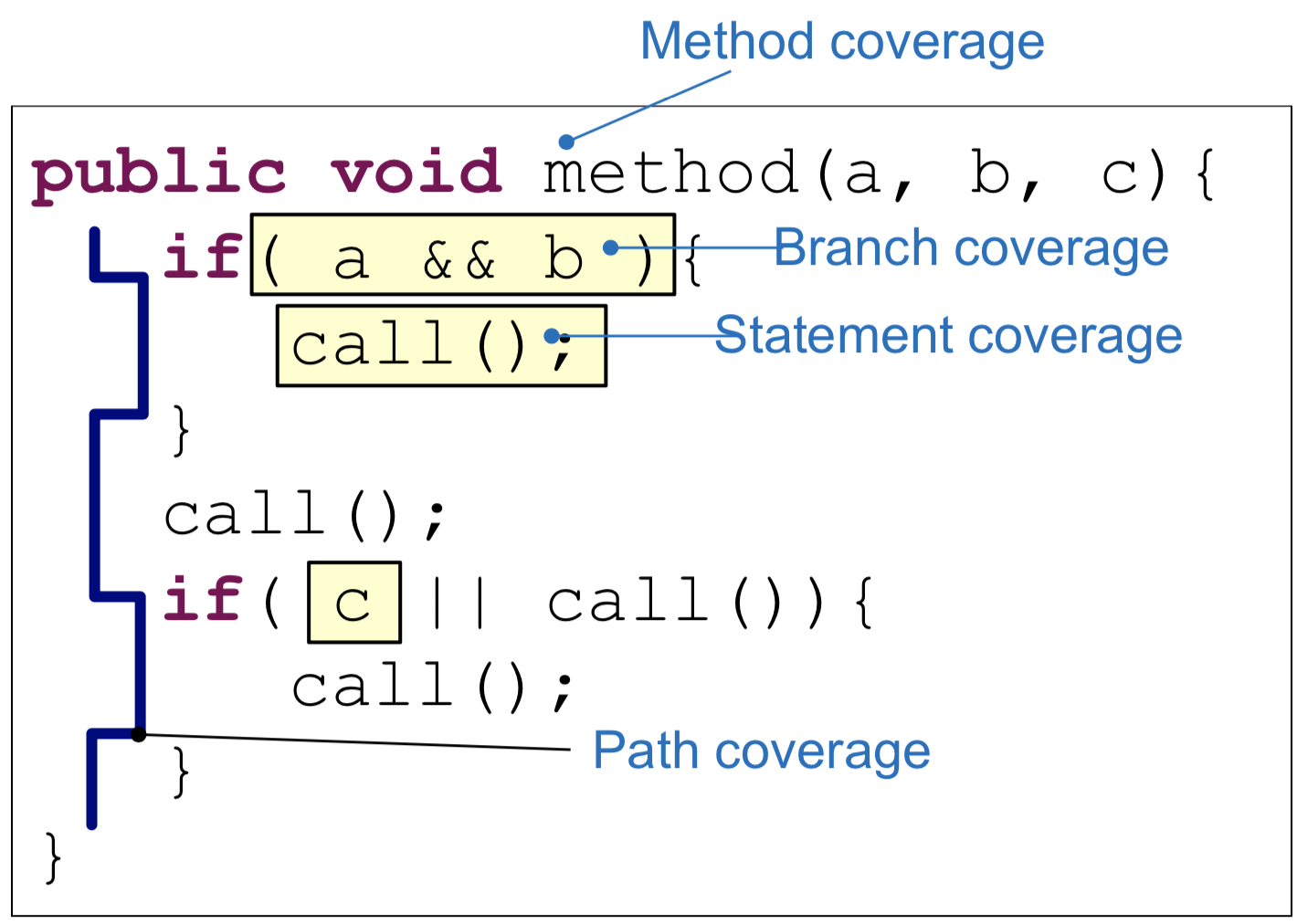
Basic Coverage Criteria
洋葱模型
- Class Coverage: 报告有多少类被覆盖
- Method Coverage: 报告特定 method 是否在 test 过程中被唤起
- Branch Coverage: 报告一个布尔表达式的真假结果
- Statements/Line Coverage: 报告一行代码是否被执行
- Instruction Coverage: 对于 JVM 来说,method 的 字节流就是一系列的指令,这个字节流会被执行
Equation for Computing Coverage
Code Coverage Analysis Process
- 写 test 然后执行
- 查看哪些代码没被 test 覆盖到
- 给那些代码写新的 test
Mutation Testing
“Code Coverage 会给人一种虚假的安全感”
Why Mutation?
- 用来模拟典型的语法错误
- 突变体 mutants 总是要对抗那些 test 以达成测试的质量
- The tests are attributed a score between 0 and 1, as to whether they can distinguish between the original and the mutants
mutation steps
- Create mutants
- Try to kill the mutants
如果 mutants 还活着,说明 mutants 没被测到
如果 mutants 死了,就是测到了
L6
Maven
DEF: A a project management and comprehension tool
Provide ways to help with managing:
- Builds
- Documentation
- Reporting
- Dependencies
- SCMs
- Releases
- Distribution
Project Object Model (POM)
A Project Object Model or POM is the fundamental unit of work in Maven. It is an XML file that contains information about the project and configuration details used by Maven to build the project. It contains default values for most projects.
Maven Phases
Common default lifecycle phases:
- validate: validate the project is correct and all necessary information is available
- compile: compile the source code of the project
- test: test the compiled source code using a suitable unit testing framework. These tests should not require the code be packaged or deployed
- package: take the compiled code and package it in its distributable format, such as a JAR.
- integration-test: process and deploy the package if necessary into an environment where integration tests can be run
- verify: run any checks to verify the package is valid and meets quality criteria
- install: install the package into the local repository, for use as a dependency in other projects locally
- deploy: done in an integration or release environment, copies the final package to the remote repository for sharing with other developers and projects.
There are two other Maven lifecycles of note beyond the default list above. They are
- clean: cleans up artifacts created by prior builds
- site: generates site documentation for this project
Evosuite
Generating JUnit tests automatically
Who is the author?
- Andrea Arcuri
- Prof. Xin Yao’s (妮可CS系主任) previous students
DEF: EvoSuite uses evolutionary algorithm to generate and optimize whole test suites towards satisfying a coverage criterion.
演化的三大要素:Crossover, Mutation, Fitness
METRICS
To measure product and project progress
NON-TECHNICAL METRICS
- 组队人数
- 总时间消耗,花费
- Bug 被找到的、被报告的
- 测试人员,开发者
- 用户
- Bug 修复的,实现多少功能 features
TECHNICAL METRICS
- 代码有多少
- 文件数量
- 类数量
- 进程数量
- 代码复杂度
- Dependencies / Coupling / Cohesion
- Depth of nesting
- Cyclomatic complexity·
MEASURING SIZE OF SYSTEM
代码行数
复杂度
Cyclomatic complexity (Thomas J. McCabe, Sr. in 1976)
- = Number of branches (if, while, for) + 1
Function points
- Count number of inputs, number of outputs, number of algorithms, number of tables in database
Coupling (关联 dependences among modules) and cohesion (聚合 dependences within modules)
- Dependences: Call methods, refer to class, share variable
- Coupling - bad
- Cohesion - good
- shared variables 的数量和复杂度
- 模块内的函数应该共享变量
- 模块间则不能
- 参数的数量和复杂度
- 被调用的函数、模块的数量
- 调用自己的函数、模块的数量
1 | Module coupling = 1 / ( |
数值越低,coupling 越高
- Ca : 传入耦合 Afferent coupling: 外部类的数量-依赖模块内部类
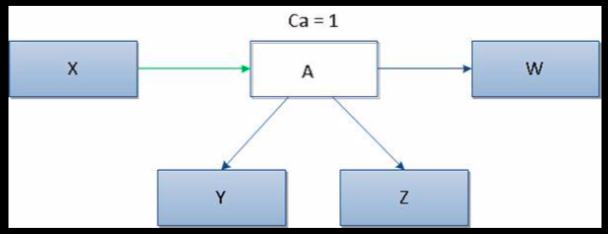
- measure the sensitivity of remaining packages
- 高值说明有很强的组件稳定性
- Ce : 传出耦合 Efferent coupling: 内部类的数量-依赖外部类
- /lecture/rev/https://i.loli.net/2019/06/10/5cfde1761fc3719289.png)
- measure the vulnerability of the package
- > 20 说明有很高的不稳定性
INSTABILITY
ABSTRACTNESS
Many OO-specific metrics
-
Weighted Methods Per Class (WMC)
-
是指类中所有 method 的复杂性的和
- 可能的 method complexities
• 1 (number of methods)
• Lines of code
• Number of method calls
• Cyclomatic complexity
- 可能的 method complexities
-
-
Depth of Inheritance Tree (DIT)
-
inheritance 依赖关系树,一个类到其根节点的最长距离
-
Number of Children (NOC)
- Number of immediate subclasses
-
Coupling between Object Classes (CBO)
- 所有 coupled 的其他类的数量 Number of other classes to which a class is coupled
- 在本类的一个方法中 invoke 其他类的方法,就算一个
- Coupling 使得难以改变设计
- Coupling 使得难以复用 classes
-
Response for a Class (RFC)
- 一个类中可能被 object of that class 调用的 method
- 越多越复杂
-
Lack of Cohesion in Methods (LCOM)
USE METRICS
-
衡量一个人写了多少代码
-
衡量模块复杂性
-
决定一个系统需要多少行代码的 function points
-
跟进整体进度
- SLOC 增长
- 报告的,修复的 bugs 数量
- SLOC per function point (user story)
SLOC per programmer (user stories per programmer)
-
code review
-
planning
-
predict amount of effort / components and SLOC / stories & months (XP)
-
Opinion of related people
L9
逆向工程 REVERSE ENGINEERING
Terms:
- Forward engineering: From requirements to design to code
- Reverse engineering: From code to design, maybe to requirements
- Reengineering: From old code to new code via some design
Read alll code in 1 hour
- Intent: 很笼统但具有目的性的去读代码
- Problem: 系统很庞大、多样化,不熟悉
- Solution: read code & document findings (important entities, “code smells”, tests)
- Hints: what to look for?
- 代码风格, tests (system and unit)
- Abstract classes or classes high in hierarchy
- Large entities, comments
PATTERNS FOR INITIAL UNDERSTANDING
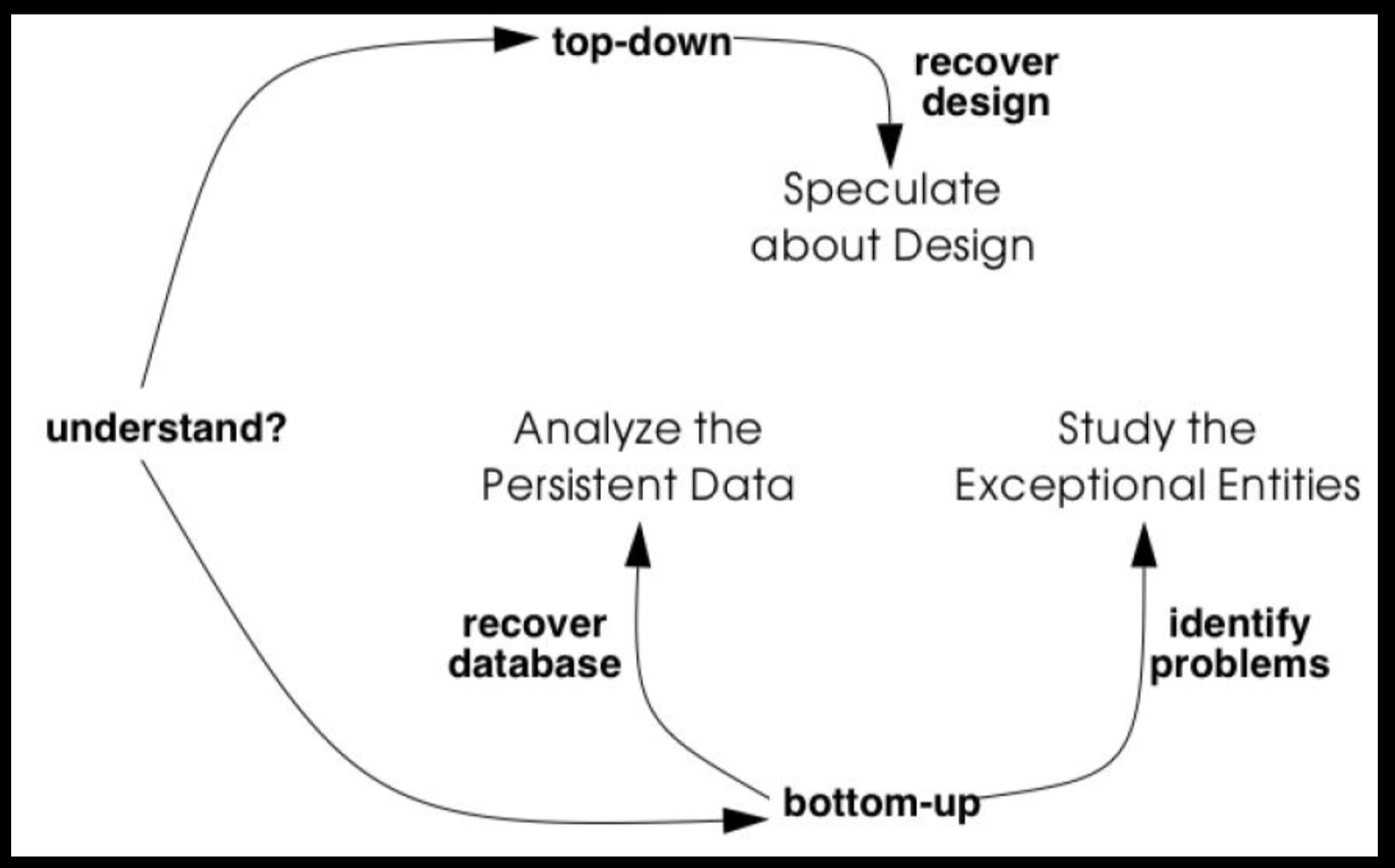
PATTERNS FOR INITIAL UNDERSTANDING
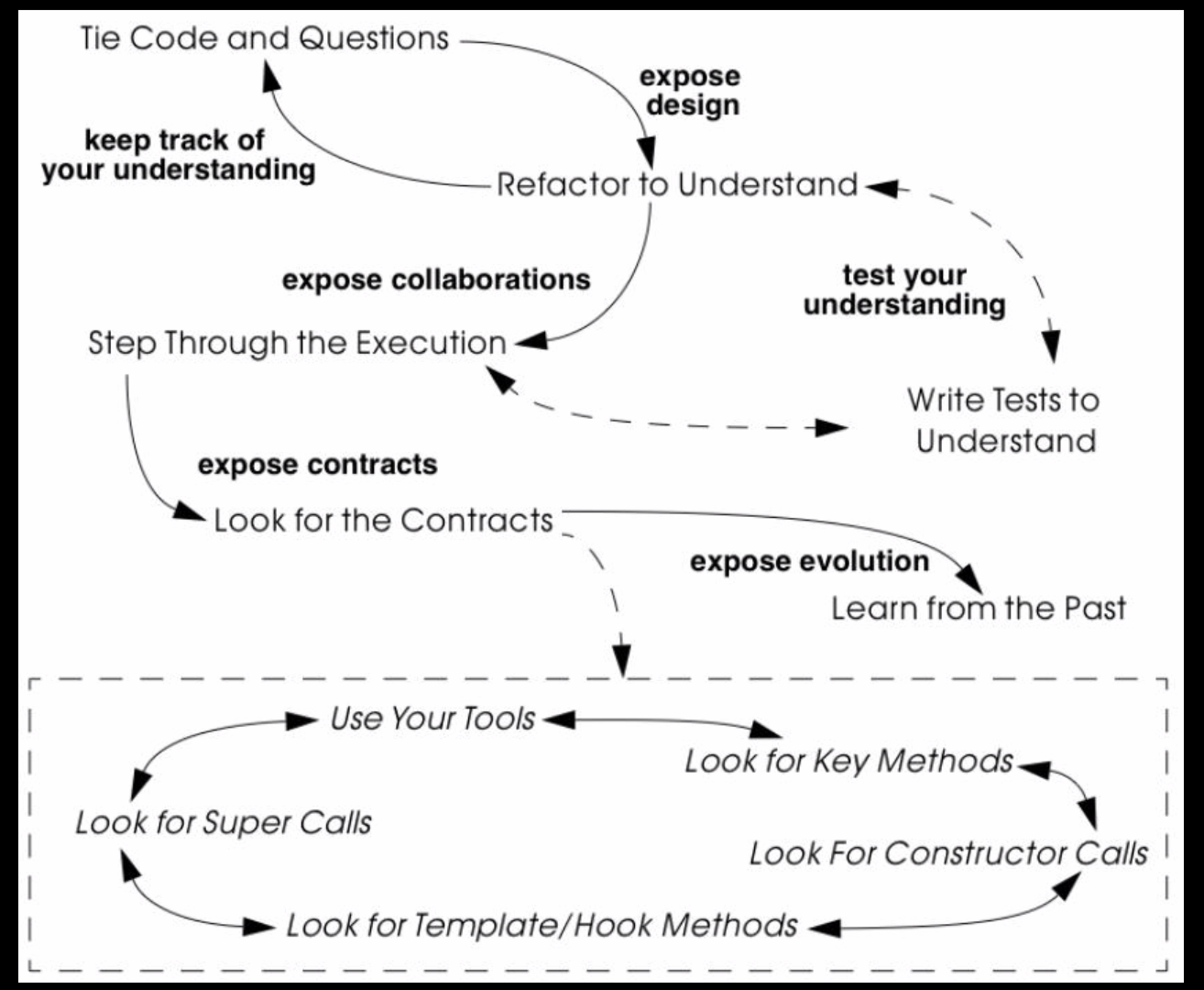
REVERSE ENGINEERING ACTIVITIES
目的:Learn the system from the system
行为
- Read documentation
- Talk to people
- Look at the code
- Work with the system
- Write documentation
规划一个大致的框架
类的 hierarchy
Modules
Tools
Diagramming tools (Java → UML class diagram / C → call graph / ……)
Code browsers
Debuggers
逆向工程的 METRICS
- Coupling
• Top layers depend on lower layers
• Lower layers do not depend on anything - Frequent changes
• git changes 中 影响一个模块的百分比 (class) - Bugs
• Code coverage
代码浏览器
读代码用的工具
交叉引用
交互
Debuggers
看代码如何执行
Singlestep
断点
DEALING WITH SIZE
• Get an overview
• Decompose
• Examine each part individually
• Experiment to test knowledge
• Correct overview
Documentation
已知文档
- 需求
- 架构总体概观
- 组件设计
- 接口描述
- user manual
- 注释
写文档
- 描述已经存在的
- 描述需要学习的
- 简化和抽象
- 描述问题、总体设计、细节、例子
TESTS
测试可以是文档,运行测试帮助理解系统流程,帮助学习
逆向工程 SUMMARY
- Reverse engineering is analyzing an existing system
- Instead of inventing design ideas, discover them
- Tools useful, but people are more important and hard work is essential
L10
Testing
Static Analysis
-No dynamic excution
-Detect possible detects in an early stage
Tools
• Checkstyle
• PMD
• FindBugs
Checkstyle
Focus on Java coding style and standards.
- whitespace and indentation 空格&缩进
- variable names 变量名称
- Javadoc commenting
- code complexity
- number of statements per method
- levels of nested ifs/loops
- lines, methods, fields, etc. per class
- proper usage
- import statements 导入顺序
- regular expressions 正则
- exceptions
- I/O
- thread usage, …
PMD
- 检查可能的 bug: empty try/catch/finally/switch statements
- 检查无用代码:未使用的本地变量,参数,和私有方法
- 检查劣质代码 Suboptimal code: wasteful String/StringBuffer usage
- 检查过于复杂的表达式:非必要的 branch & loop
- 检查重复的代码
FindBugs
A bug pattern is a code idiom that is often an error.
- Difficult language features
- Misunderstood API methods 没解析出来的api
- Misunderstood invariants 不变量 when code is modified during maintenance
- Garden variety mistakes: typos, use of the wrong boolean operator
使用静态分析以检查 java bytecode
不会执行程序
L11
Defensive Programming
保证没有产生 error 甚至不产生 warning 的前提下写代码是一种防御性编程
DEF:是一种防御性设计,为了确保软件的持续功能,没有不可预料的情况下,high availability, safety or security is needed.
Murphy’s Law: If anything can go wrong, it will.
Defensive Programming:
- Redundant code(多余代码) is incorporated to check system state after modifications.
- Implicit assumptions (隐式假设) are tested explicitly.
- Risky programming constructs are avoided.
有风险的结构们:要谨慎使用
- Pointers
- Dynamic memory allocation
- Floating-point numbers
- Parallelism
- Recursion
- Interrupts
例子:
- 判断的时候(如果情况只有01)不要使用整型,而使用 boolean
- Test i<=n not i==n
- 检查断言 assertion
Maintenance
Fault Tolerance
大致方法:
- Failure detection
- Damage assessment
- Fault recovery
- Fault repair
N-version programming — 并行化运行相互独立的实现,对比结果,采用最可能的一个
错误承受的一些技巧
- 发生 error 之后立即进行下一个 transaction
- Timers and timeout in networked systems
- 使用 break
- Error correcting codes in data
- Bad block tables on disk drives
- Forward and backward pointers in databases
- log 所有信息
倒推恢复 backward recovery
- Record system state at specific events (checkpoints)
- 备份
- 结合 checkpoint 与系统日志
- 当然对于 restore software 也是需要测试他的稳定性
Security in the Software Development Process
Agents and Components
Techniques:
Barriers
Authentication & Authorization
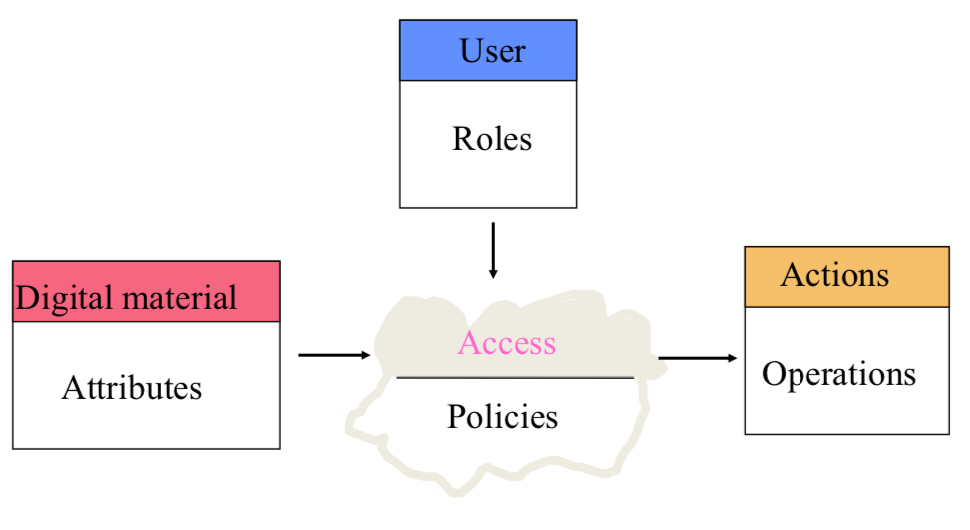
Encryption
Software Reuse and Component-Based Software Engineering
- Application System Reuse
- 复用整个应用 by incorporation of one application inside another (COTS reuse)
- development of application families (e.g. MS Office)
- Component Reuse
- 一个应用的组件 (e.g. subsystems or single objects) 在另一个应用中复用
- Function Reuse
- 复用一个函数
好处
- Increased Reliability
- 组件已经被验证可用性
- Reduced Process Risk
- 开发消耗中更小的不确定性
- Effective Use of Specialists
- 而非复用人
- Standards Compliance
- 嵌入标准
- Accelerated Development
- 避免自定义开发而加速交付
Economics
- Quality
- Productivity
- Cost
Generator-Based Reuse
Program Generation
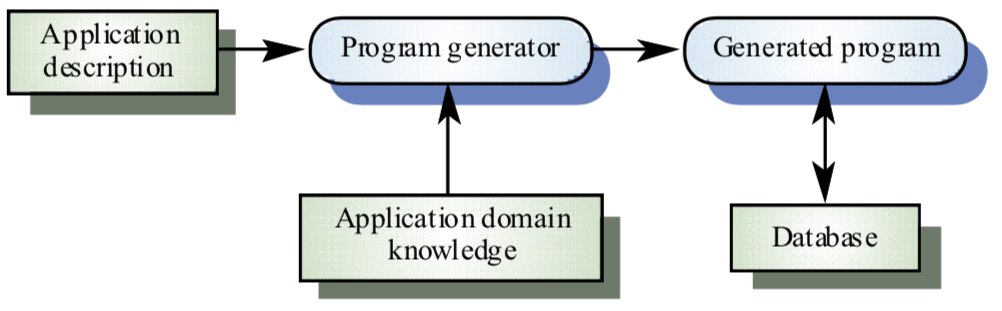
Component-Based Engineering
CBSE is an approach to software development that relies on reuse
组件抽象
- 函数抽象
- 随意组合
- 数据抽象
- 集群抽象
- 系统抽象
approach
- Software team elicits system requirements
- Architectural design is established
- Team determines requirements are amenable to composition rather than construction
- commercial off-the-shelf (COTS)
- Team attempts to remove or modify requirements that cannot be implemented with COTS or in-house components
- For those requirements that can be addressed with available components the following activities take place
- Detailed design activities commence for remainder of the system
Terms
- Component Qualification: candidate components are identified based on services provided and means by which consumers access them
- Component Adaptation: candidate components are modified to meet the needs of the architecture or discarded
- Component Composition: architecture dictates the composition of the end product from the nature of the connections and coordination mechanisms
- Component Update: updating systems that include COTS is made more complicated by the fact that a COTS developer must be involved
DEF: COTS systems are usually complete applications library the off an applications programming interface (API)
Review:
- Analysis
- Architectural design
- component qualification
- component adaptation
- component decomposition
- Component engineering
- Testing
- Iterative component update
L12
Abstraction
L13
UI-Design
10 rules of Good UI Design
- Make Everything the User Needs Readily Accessible
- Be Consistent
- Be Clear
- Give Feedback
- Use Recognition, Not Recall
- Choose How People Will Interact First
- Follow Design Standards
- Elemental Hierarchy Matters
- Keep Things Simple
- Keep Your Users Free & In Control
L14
Documentation
DevOps and Continuous Integration
Development + IT Operations
Continuous Integration is a software development practice where members of a team integrate their work frequently, usually each person integrates at least daily - leading to multiple integrations per day. Each integration is verified by an automated build (including test) to detect integration errors as quickly as possible.
10 Principles
- Maintain a code repository – version control
- Automate the build
- Make your build self-testing
- Everyone commits to mainline every day
- Every commit should build mainline on an integration machine
- Keep the build fast
- Test in a clone of the production environment
- Make it easy for anyone to get the latest executable
- Everyone can see what’s happening
- Automate deployment
L15
Regression Testing
- Continuous Integration (CI)
- Integrate Frequently
- Verified with automated build and automated testing
- Continuous Delivery(CD) = CI + Automated test suite
- Continuous Deployment = CD + Automated Deployment
L16
Security Engineering
Final Review
Terms:
| Term | Example |
|---|---|
| Asset | The records of each patient that is receiving or has received treatment. |
| Exposure | Potential financial loss from future patients who do not seek treatment because they do not trust the clinic to maintain their data. Financial loss from legal action by the sports star. Loss of reputation. |
| Vulnerability | A weak password system which makes it easy for users to set guessable passwords. User ids that are the same as names. |
| Attack | An impersonation 模仿、假扮 of an authorized user. |
| Threat | An unauthorized user will gain access to the system by guessing the credentials (login name and password) of an authorized user. |
| Control | A password checking system that disallows user passwords that are proper names or words that are normally included in a dictionary. |
Summary of SCM
- Four aspects
- Change control
- Version control
- Building
- Releasing
- Supported by tools
- Requires expertise and oversight
- More important on large projects
waterfall model

eXtreme Programming XP
- Different from the rigid waterfall process
- Replace it with a collaborative and iterative design process
- Main ideas
- Don’t write much documentation
- Working code and tests are the main written product
- Don’t write much documentation
- Implement features one by one
- Release code frequently
- Work closely with the customer
- Communicate a lot with team members
XP: Some key practices
Planning game for requirements
Test-driven development for design and testing
Refactoring for design
Pair programming for development
Continuous integration for integration
Test
Terms
MISTAKE 被程序员制造
FAULT/BUG 在程序代码中出现
FAILURE 在程序运行时发生
ERROR 就是与预期结果不符的差异
Steps in Test Driven Development (TDD)
- Quickly add a test.
- Run all tests and see the new one fail.
- Make a little change to code.
- Run all tests and see them all succeed.
- Refactor to remove duplication.
Coverage Criteria
Instructions Coverage
Statements Coverage
Branch Coverage
Method Coverage
Class Coverage
Yes, there are several popular open-source test generations
- Randoop
- Evosuite
Cyclomatic Complexity
= Number of branches (if, while, for) + 1
Martin’s Coupling Metric
- Ca : Afferent coupling: measure incoming dependencies
- Ce : Efferent coupling: measure outgoing dependecies
Instability = Ce / (Ca + Ce)
Reverse engineering
- Discovering design of an artifact
- From lower level to higher level
- trying to understand how the system works
Read All Code in 1 Hour
- Intent: assess a software system via a brief but intensive code review
- Problem: system is large/varied, unfamiliar
- Solution: read code & document findings (important entities, “code smells”, tests)
- Hints: what to look for?
- Coding styles/idioms, tests (system and unit)
- Abstract classes or classes high in hierarchy
- Large entities, comments
Patterns for Initial understanding

Patterns For Detailed model capture

What is testing?
- Dynamic Analysis
- Static Analysis
Tools for Static Analysis
• Checkstyle
• PMD
• FindBugs
10 rules of Good UI Design
- Make Everything the User Needs Readily Accessible
- Be Consistent
- Be Clear
- Give Feedback
- Use Recognition, Not Recall
- Choose How People Will Interact First
- Follow Design Standards
- Elemental Hierarchy Matters
- Keep Things Simple
- Keep Your Users Free & In Control
Doc
Rules for writing summaries
- The first sentence should summarize the purpose of the element
- For methods, omit the subject and write in the third-person narrative form
- Good: Finds the first blank in the string.
- Not as good: Find the first blank in the string.
- Bad: This method finds the first blank in the string.
- Worse: Method findBlank(String s) finds the first blank in the string.
- Use the word this rather than “the” when referring to instances of the current class (for example, Multiplies this fraction…)
- Do not add parentheses to a method or constructor name unless you want to specify a particular signature
- Keep comments up to date!
DevOps
= Development + IT Operations
Smoke Test
A quick set of tests run on the daily build.
- Cover most important functionalities of the software but NOT exhaustive
- Check whether code catches fire or “smoke” (breaks)
- Expose integration problems earlier
Continuous Integration & Continuous Deployment
Design -> Code -> Build -> Integrate -> Test -> Release -> Deploy
- Agile Development 短————>
- Continuous Integration ————————>
- Continuous Delivery ——————————————>
- Continuous Deployment 长————————————————>
